Difference: HardwareAccessAndMicropython (3 vs. 4)
Revision 42019-05-14 - UliRaich
| Line: 1 to 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Slide 1: Setting up and IoT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line: 41 to 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
How to program the processor | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > |
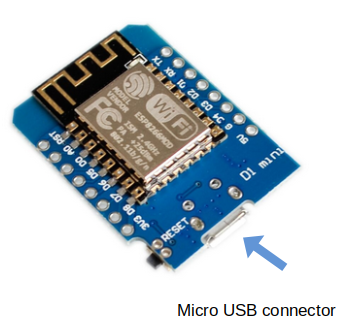
Flashing the code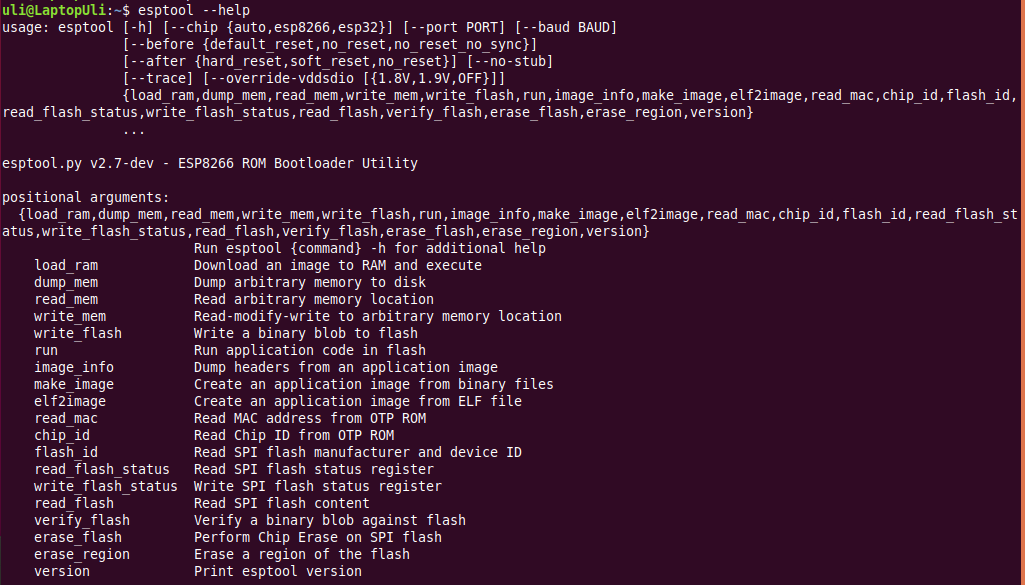
esptool
How to write a Micropython program?First we need a Micropython interpreter! You find the sources here: https://github.com/micropython/micropython/How to communicate with the Micropython interpreter?We use a serial connection passing through the micro USB connection. As soon as we connect the processor card to the PC we see the UART bridge and a new device: dev/ttyUSB0 is created. This device is used to communicate with the Micropython REPL.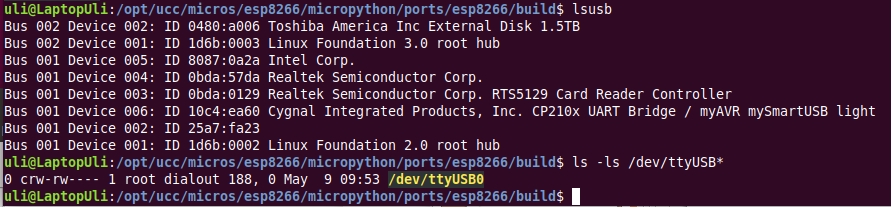 You see the command prompt and you can interact with Micropython. But … how to upload scripts?
You see the command prompt and you can interact with Micropython. But … how to upload scripts?
What is REPL?
The communication tools: minicom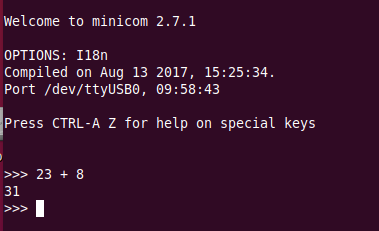 You see the command prompt and you can interact with Micropython.
But … how to upload scripts?
You see the command prompt and you can interact with Micropython.
But … how to upload scripts?
The command line tool ampy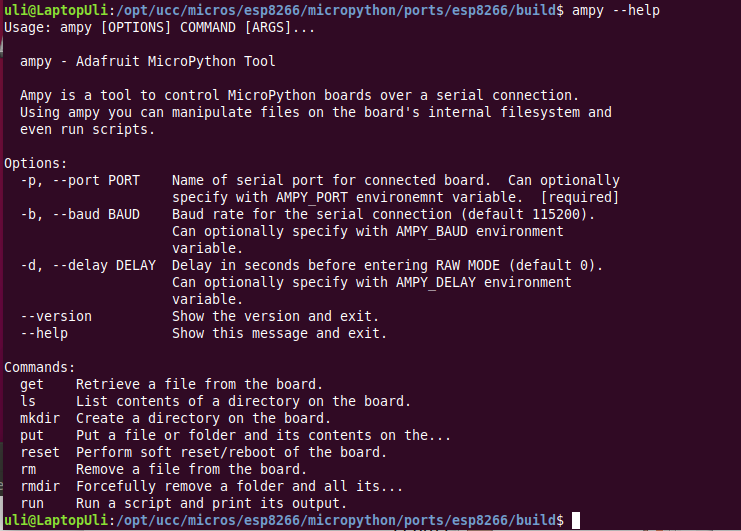
IDE for Micropython: uPyCraft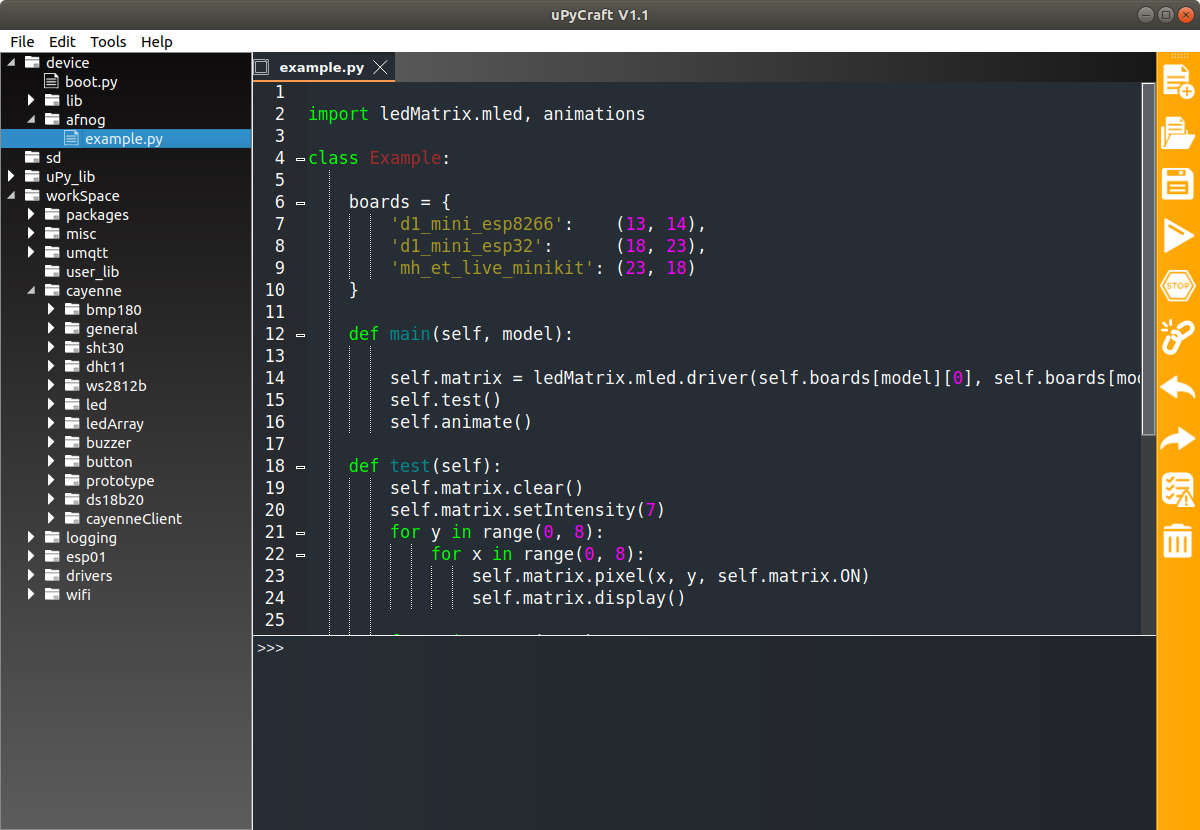
uPyCraftuPyCraft is a rather complete Integrate Development Environment (IDE) which lets you
Flashing MicropythonThis has already been done for you! However, it is easy if you want to do it at home with a new processor board. Compiling a new version of Micropython is substantially harder but also perfectly possible.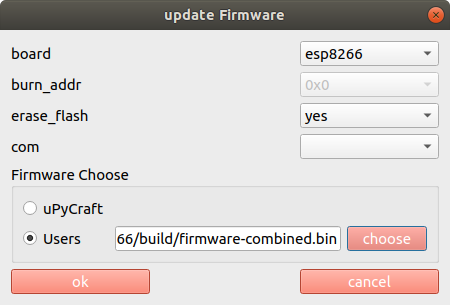
uPyCraft(2)uPyCraft is based on QT4 and is available for Linux, Windows and Mac. It is written in PyQt4 the Python language binding to Qt4. The Linux version did not work for me I found a version based on PyQt5 (new version of QT) which was even worse. I tried to correct as much as I could to make the PyQt5 version usable on Linux: https://github.com/uraich/uPyCraft-Qt5Thonny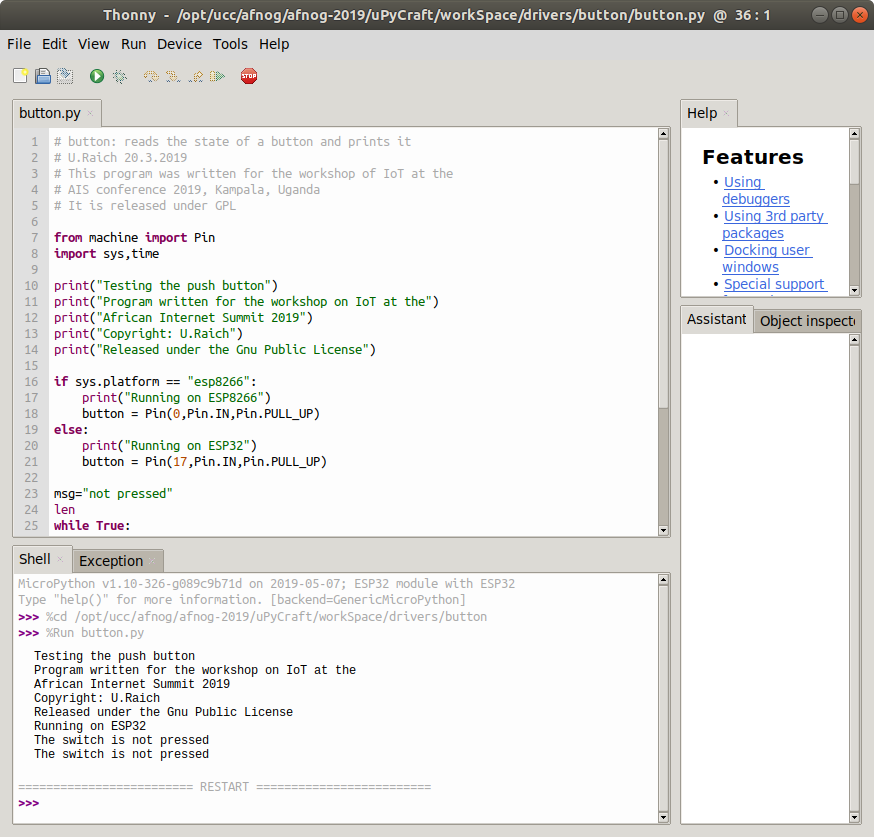
Thonny (2)Thonny is an IDE for Python which has provisions for Micropython.Under Tools → Options button you can select the type of Python interpreter you intend to use. 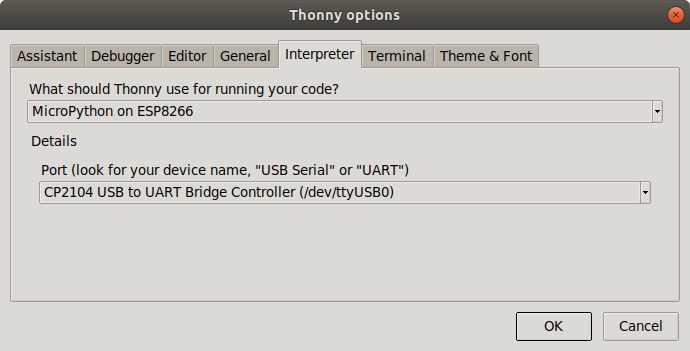
IoT Hello World programA “Hello World” program, just printing “Hello World” on the screen does not look very exciting. However, this is generally used to verify that the infrastructureCompiler, linker, downloader, flash program are working correctly In embedded systems printing can be quite complex and a blinking LED is used instead. Switching on and off a LEDThe ESP8266 and the ESP32 have a “user LED” connected to GPIO 2. How do we control this LED?
Micropython hardware functions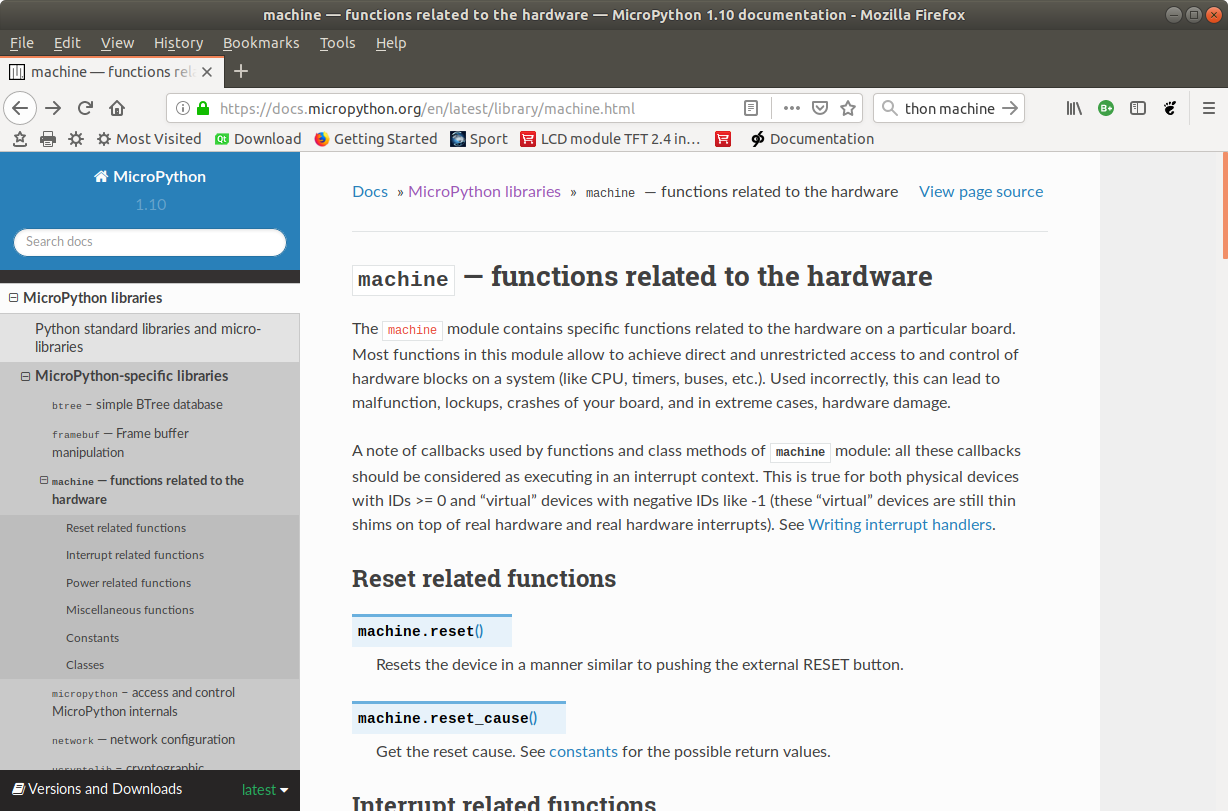
The machine.Pin class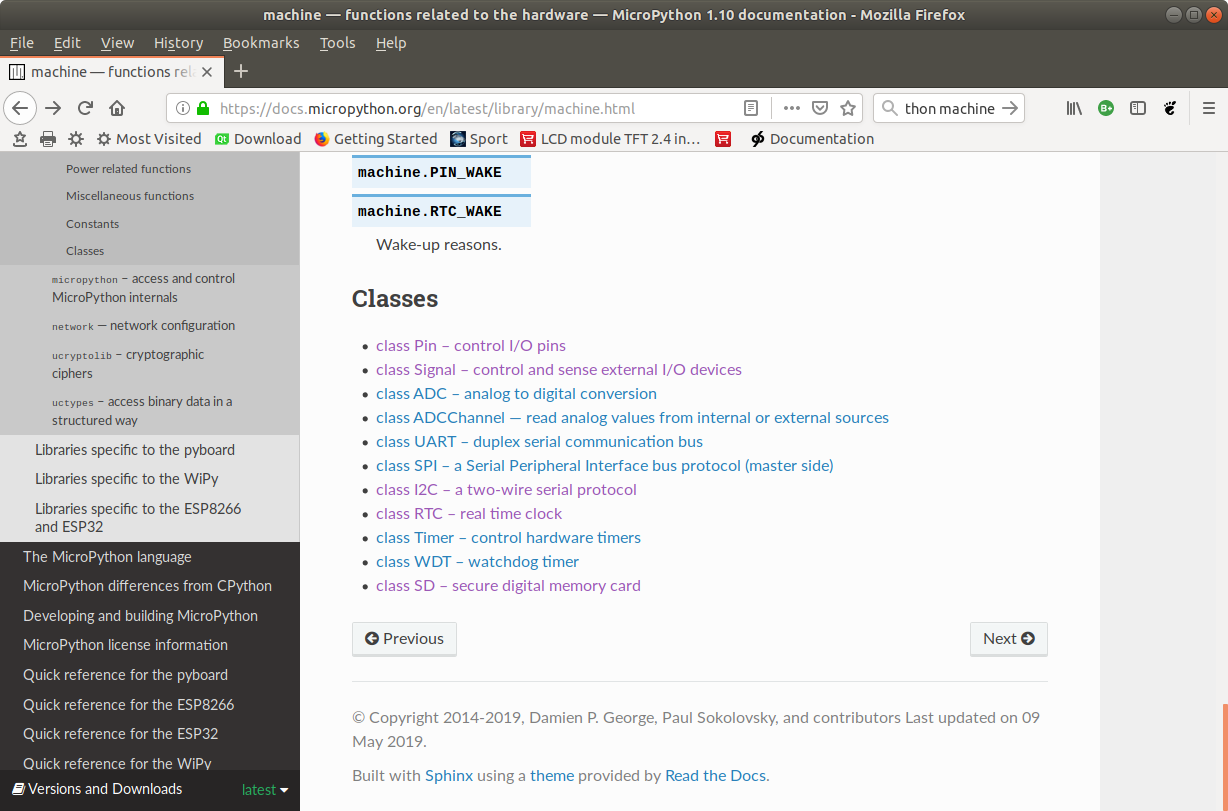
Switch the LED on, version 1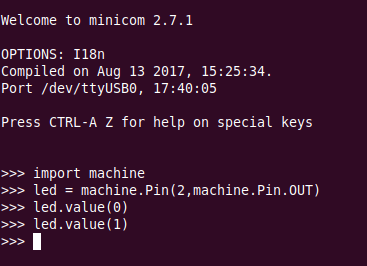
Switch the LED on, version 2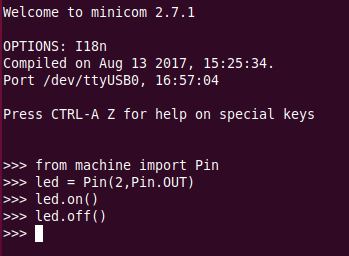
The blinking LEDNow we put the code into a script and run it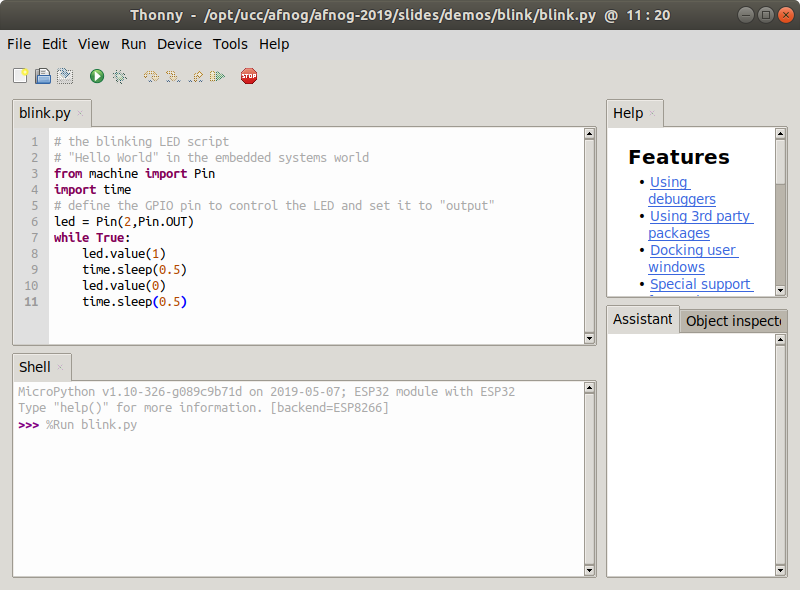
Changing the light intensityThe LED is connected to a digital line which can only be set to 0 or Vcc. How can we change the light intensity and dim the LED? The light intensity depends on the average current flowing through the LED. The answer is PWM: pulse width modulation.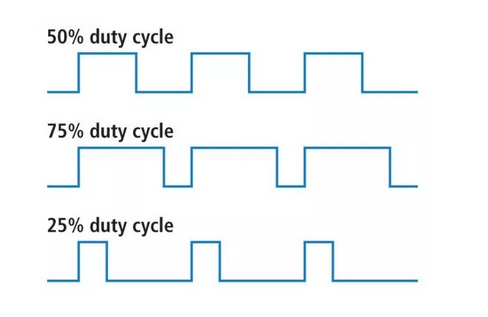
PWM in Micropython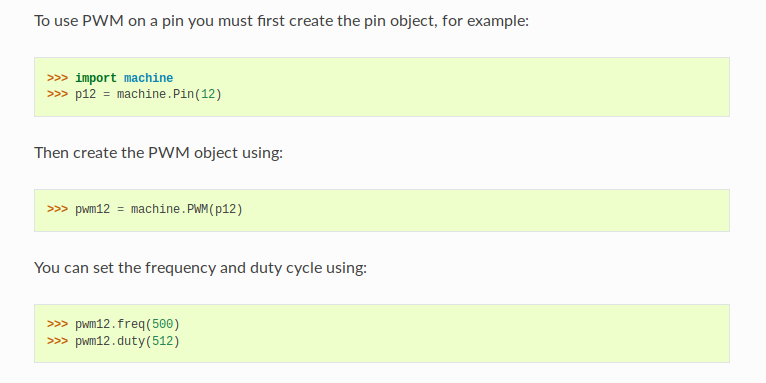
Our PWM implementation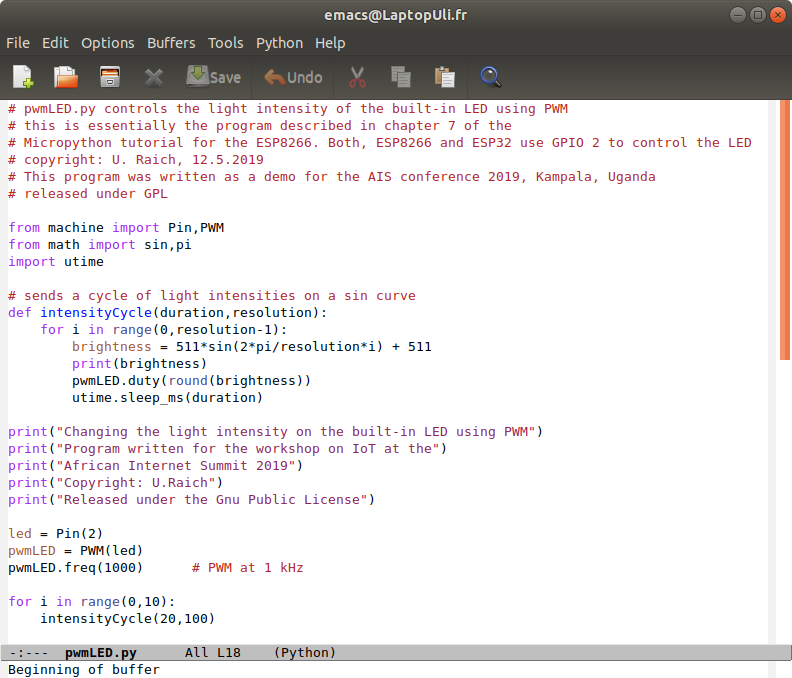
The WS2812B LEDA more complex LED:
WS2812B timingFor all the details on the ws2812b look athttps://cdn-shop.adafruit.com/datasheets/WS2812B.pdf 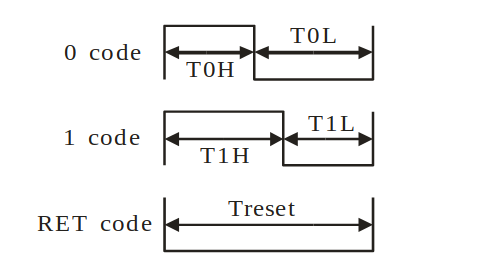 The control word:
The control word:

Cascading the WS2812B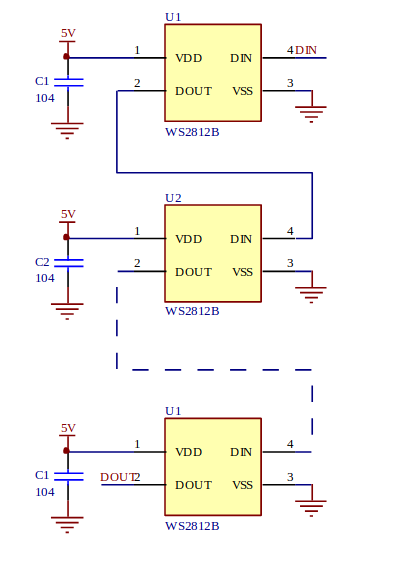
Using the neopixel library… and our codeWe have a single neopixel connected to GPIO pin 4 (ESP8266) or GPIO pin 21 (ESP32) This code works on both CPUs! | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| %SLIDESHOWEND% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line: 60 to 312 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Added: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
View topic | History: r7 < r6 < r5 < r4 | More topic actions...
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback