
Difference: InternetAccess (5 vs. 6)
Revision 62020-06-04 - UliRaich
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Internet accessOnce we have collected data from the sensors we want to get access to them. This can be accomplished most easily by transferring the data over the Internet. Most of the time we also want to plot the data in some form or another. Often it is also desired to see real time data.WiFi | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | Before doing anything on the Internet we must first connect the ESP32 to the WiFi network. The module: | |||||||
| > > | The WeMos D1 mini ESP32 CPU board offers WiFi access implementing a TCP/IP and full 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi MAC protocol (see the ESP32 data sheet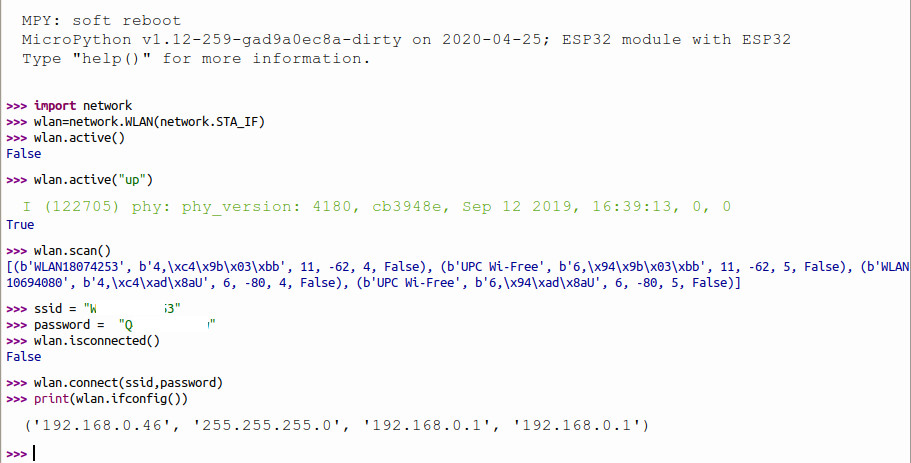 All you need to do is putting in the correct ssid for your WiFi network and the corresponding password. Of course you do not want to type all this each time you connect to your network and for this reason a wifi_connect.py module is already included in your MicroPython binary.
All you need to do is putting in the correct ssid for your WiFi network and the corresponding password. Of course you do not want to type all this each time you connect to your network and for this reason a wifi_connect.py module is already included in your MicroPython binary. | |||||||
| https://afnog.iotworkshop.africa/pub/IoT_Course_English/InternetAccess/wifi_connect_public.py.txt | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
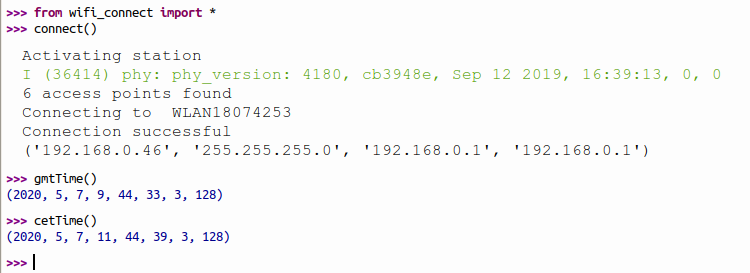
| < < | provides all necessary functions to do this. It first connects to WiFi as a station interface and print the IP address it is connected to. If it is already connected it simply returns. Once connected it gets the current time from the NTP time server and sets up the ESP32 real time clock. You can get the current GMT time with gmtTime() or CET time with cetTime(). The module is already included in the MicroPython binary. | |||||||
| > > | provides all necessary functions to do this. It first connects to WiFi as a station interface and prints the IP address it is connected to. If it is already connected it simply returns. Once connected it gets the current time from the NTP time server and sets up the ESP32 real time clock. You can get the current GMT time with gmtTime() or CET time with cetTime(). The module is already included in the MicroPython binary. | |||||||
 | ||||||||
| Line: 19 to 25 | ||||||||
|
Since I cannot know the SSID and password of your WiFi network, connect() will only work for my private network. You can however pass your SSID and password as parameters: connect(ssid="YourSSID",password="YourWiFiPasswword") | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | You can get the IP address allocate with | |||||||
| > > | You get the IP address allocate with | |||||||
getIPAddress().
An FTP server | ||||||||
| Line: 42 to 48 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
View topic | History: r10 < r9 < r8 < r7 | More topic actions...
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback