
Difference: MoreSensors (1 vs. 7)
Revision 72018-12-21 - UliRaich
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Additional Sensors | ||||||||
Revision 62018-11-27 - UliRaich
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Additional Sensors | ||||||||
| Line: 16 to 16 | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | ||||||||
| > > | ||||||||
|
The Raspberry Pi uses I2C bus 1 for communication with external I2C devices. This can be seen in the /dev directory. Both libraries: wiringpi | ||||||||
Revision 52017-02-14 - uli
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Additional Sensors | ||||||||
| Line: 15 to 15 | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
|
The Raspberry Pi uses I2C bus 1 for communication with external I2C devices. This can be seen in the /dev directory. Both libraries: wiringpi | ||||||||
Revision 42017-02-05 - uli
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Additional Sensors | ||||||||
| Line: 11 to 11 | ||||||||
The additional sensor boards are all based on the I2C bus and include
| ||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
The Raspberry Pi uses I2C bus 1 for communication with external I2C devices. This can be seen in the /dev directory. Both libraries: wiringpi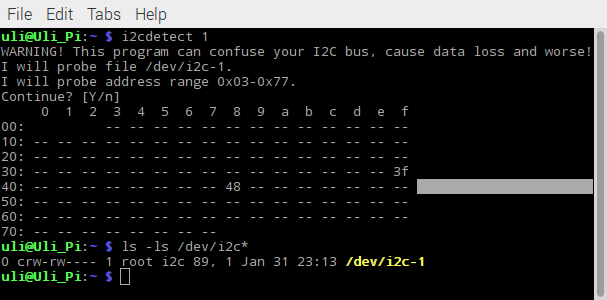 | ||||||||
Revision 32017-02-01 - uli
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Additional Sensors | ||||||||
| Line: 8 to 8 | ||||||||
| The sensor kit contains 2 sensors with analogue to digital conversion on the sensor chip (DS18b20 and DHT11) while for other analogue signals an additional external ADC is needed. | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | The additional sensor boards are all based on the I2C bus and include | |||||||
| > > | The additional sensor boards are all based on the I2C bus and include | |||||||
| ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | The Raspberry Pi uses I2C bus 1 for communication with external I2C devices. This can be seen in the /dev directory. Both libraries: wiringpi | |||||||
| > > | The Raspberry Pi uses I2C bus 1 for communication with external I2C devices. This can be seen in the /dev directory. Both libraries: wiringpi | |||||||
 | ||||||||
Revision 22017-02-01 - uli
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Additional Sensors | ||||||||
| Line: 16 to 16 | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | The Raspberry Pi uses I2C bus 1 for communication with external I2C devices. This can be seen in the /dev directory. Both libraries: wiringpi | |||||||
-- Comments | ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||
Revision 12017-02-01 - uli
| Line: 1 to 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > |
Additional SensorsThe sensor kit was originally designed to be used with the Arduino, an Italian micro-controller design very popular with hobbyists. The Arduino uses Atmel micro-controllers with internal flash memories, which can be programmed from a PC through USB. A complete GUI based Software Development Kit (SDK) is available containing editor, cross-compiler and flash programmer. The Arduino is delivered with a boot loader pre-installed which helps in flash programming. Without this boot loader and external flash programmer is needed. The Arduino is much less powerful than the Raspberry Pi but has similar interfaces to the outside world: GPIO, SPI, I2C. In addition to the Raspberry the Arduino has 6 analogue inputs with and analogue to digital converter on chip. This allows to read analogue signals without additional hardware. The sensor kit contains 2 sensors with analogue to digital conversion on the sensor chip (DS18b20 and DHT11) while for other analogue signals an additional external ADC is needed. The additional sensor boards are all based on the I2C bus and include
Comments | |||||||
View topic | History: r7 < r6 < r5 < r4 | More topic actions...
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback