Stepping Motor Exercises
Goal:
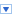
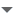
A stepping motor is a device which is often used when a precise amount of movement is required: an exact angle of a an exact position on a linear scale. While DC motors move while they a powered a stepping motor requires a sequence of impulses to move step by step as its name suggests. In this exercise we will learn how to program different step sequences for full step of half step movement and how to move the motor forward and backward. This is a photo of the motor itself and its driver module featuring an ULN2803 driver chip.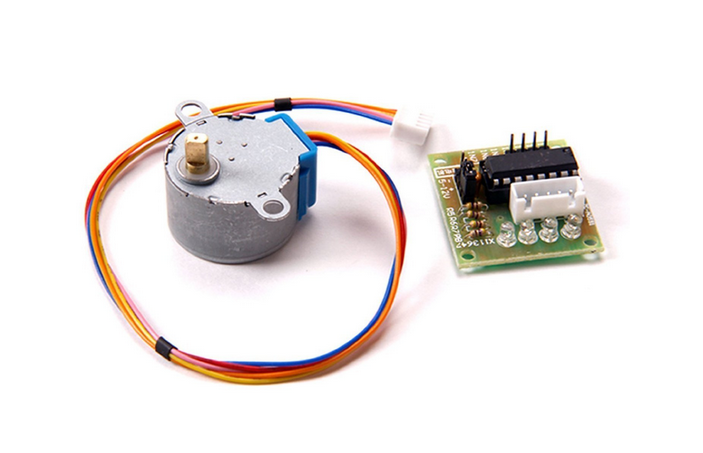
Exercise 1: Make sure the connections are correct
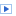
The stepping motor is has 5 connections which are provided by the cable from the driver module to the motor itself. The 2 coils must be energized in the right order.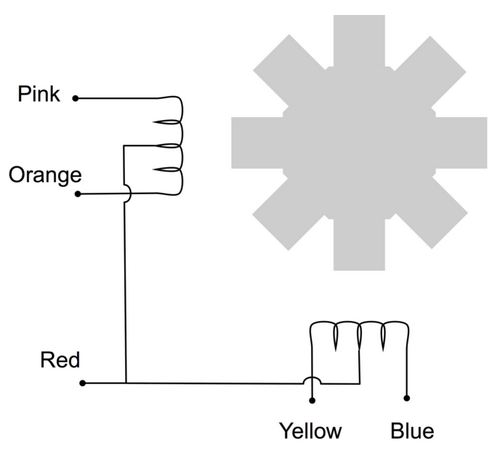 To do this we have 6 connections from the driver board to the Raspberry Pi:
To do this we have 6 connections from the driver board to the Raspberry Pi: -
5V (check for “5V +” and “-” on the board)
-
Gnd
-
4 phases denominated In0..In3
| In0 | In1 | In2 | In3 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Exercise 2: Write a program to move the stepping motor by 512 steps.
The above sequence must be sent to the stepping motor to make it move 1 full step. Make sure to wait at least 25 ms in between each setting:-
set 1 0 0 0, wait 25ms
-
set 0 1 0 0, wait 25 ms …
Exercise 3: Improve your program to give user control over its parameters
Modify your program in such a way that the user can define its behavior through command line parameters:-
-f or –forward: move forward (this is the default)
-
-b or –backward: move backward
-
-n or –numberOfSteps: number of steps (default 512)
-
-v or –velocity: velocity of movement
-
-s or –fullStep: full step (this is the default)
-
-h or –halfStep: half step
Comments
--
Comments
| I | Attachment | History | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
stepping.png | r1 | manage | 182.9 K | 2017-05-11 - 12:22 | UnknownUser | |
| |
windings.png | r1 | manage | 28.7 K | 2017-05-11 - 12:22 | UnknownUser |
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback